Admissions
Looking for a small, close-knit campus filled with incredible, hands-on learning opportunities? Our Admissions Office can help make Elmira College YOUR place.
Welcome
About EC
Getting Started
Academic Resources
Apply to EC
Visit Campus
Tuition & Financial Aid
Campus Life
Outcomes & Careers
Athletics
Alumni

Grounded in the liberal arts and sciences, Elmira College provides a collaborative and supportive environment that enables students to become active learners, effective leaders, responsible community members, and globally engaged citizens.

The legacy of academic excellence at Elmira College runs deep with a heritage and culture that have been forward-thinking from day one, as the first college for women with a course study equivalent to men's.
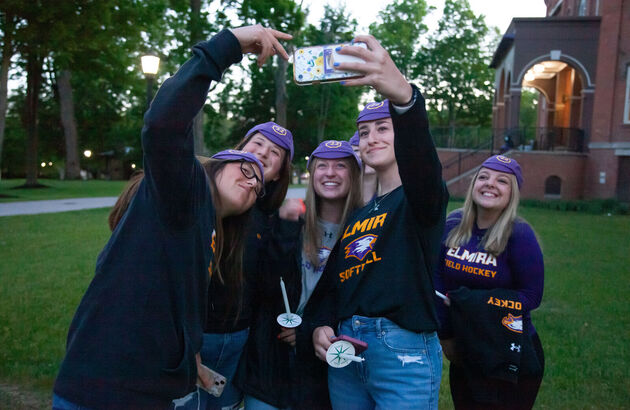

At Elmira, you’ll have opportunities that shape your future, raise your sights and equip you with targeted tools and skills to succeed in the professional world. Join a community that’s close-knit, fun-loving, and just the right amount of quirky.
Elmira College makes a private education more affordable than you realize, with a number of ways to get the financial assistance you may need. Our financial aid office can guide you through options, including scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs.

Elmira College includes meeting students from around the world, participating in Elmira traditions, completing community service projects, and hopping into a pickup kickball game.

Elmira College provides you with a foundation for future success.
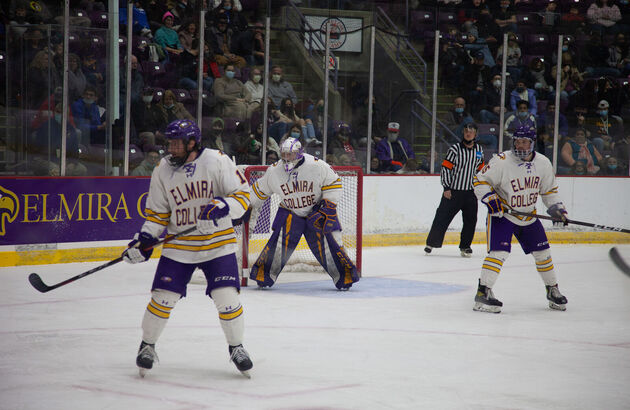

The home of the three-time NCAA National Champion Elmira College Soaring Eagles.

Elmira College alumni stay connected and engaged with the College long after they graduate.

Gifts to Elmira College ensure excellent academic and co-curricular opportunities for generations of EC students.

Looking for a small, close-knit campus filled with incredible, hands-on learning opportunities? Our Admissions Office can help make Elmira College YOUR place.

Looking for registration deadlines, spring break or when grades are due? Our academic calendar has all of the important events for this academic year.

With over 35 majors and minor areas of concentration, Elmira College lays the foundation for a diverse, cross discipline education, encouraging you to both specialize and explore.

The EC campus map can help you find your way around campus and find the best parking spot.
Internal dashboard for EC news, events, resources, and more. Log-in required.

Check out our news section to learn about all that's going on at Elmira College.
Info For








As you're applying, you may encounter some new-to-you terms related to financial aid. We put together a glossary of terms for some of the common words and phrases that will help you as you apply for aid.
This is not an extensive list of terms so if you have any questions, please reach out to the Office Of Financial Aid and we are happy to help.
Cost of Attendance (COA)
The Cost of Attendance (COA) is a college's estimate of a student's total yearly educational expenses, including both billed (direct) costs like tuition, fees, and on-campus housing, and living (indirect) costs such as books, supplies, transportation, and personal expenses.
Federal Direct Loans
Direct Subsidized Loan: Loans that the U.S. Department of Education pays the interest on while you’re in school at least half-time, for the first six months after you leave school (referred to as a grace period), and during a period of deferment (a postponement of loan payments). Direct Unsubsidized Loan: Loans that the borrower is responsible for paying the interest on during all periods. If you choose not to pay the interest while you are in school and during grace periods and deferment or forbearance periods, your interest will accrue (accumulate) and be capitalized (that is, your interest will be added to the principal amount of your loan).
Student Aid Index (SAI)
A number used by your school to calculate the amount of federal student aid you are eligible to receive. It is based on the financial information provided in your Free Application for Federal student Aid (FAFSA). This is not the amount of money your family will have to pay for college, nor is it the amount of federal student aid you will receive.
Federal Work-Study
A federal student aid program that provides part-time employment while the student is enrolled in school to help pay his or her education expenses. The student must seek out and apply for work-study jobs at his or her school. The student will be paid directly for the hours he or she works and may not automatically be credited to pay for institutional tuition or fees. The amount you earn cannot exceed the total amount awarded by the school for the award year. The availability of work-study jobs varies by school. Please note that Federal Work-Study earnings may be taxed in certain scenarios; however the income you earn will not be counted against you when calculating your Student Aid Index on the FASFA.
Graduation Rate
The percentage of students who graduate from an institution. This shows students who began their studies as first-time, full-time degree- or certificate-seeking students and completed their degree or certificate within 150 percent of "normal time." For example, for a four-year school, the graduation rate would be the percentage of students who completed that program within six years or less.
Grants and Scholarships
Student aid funds that do not have to be repaid. Grants are often need-based, while scholarships are usually merit-based. Occasionally, you might have to pay back part or all of a grant if, for example, you withdraw from school before finishing a semester. If you use a grant or scholarship to cover your living expenses, the amount of your scholarship may be counted as taxable income on your tax return.
Loans
Borrowed money that must be repaid with interest. Loans from the federal government typically have a lower interest rate than loans from private lenders. Federal loans, listed from most advantageous to least advantageous, are called Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and Direct PLUS Loans. You can find more information about federal loans at StudentAid.gov.
Loan Default Rate
The percentage of student borrowers who are more than 270 days late on their federal student loan payments.
Median Borrowing
The amount in federal loans the typical undergraduate student takes out at a particular institution. It also indicates the monthly payments that an average student would pay on that amount using a 10-year repayment plan.
Net Price
An estimate of the actual cost that a student and his or her family need to pay in a given year to cover education expenses for the student to attend a particular school. Net price is determined by taking the institution's cost of attendance and subtracting any grants and scholarships for which the student may be eligible.
Non-Federal Private Education Loan
A private education loan is a loan issued expressly for postsecondary education expenses to a borrower (either through the educational institution or directly to the borrower) from a private educational lender, rather than as a Title IV, HEA loan offered by the Department of Education.
Origination Fees
An upfront fee charged by a lender for processing a new loan application. It is compensation for putting the loan in place. Origination fees are quoted as a percentage of the total loan.
Parent PLUS Loan
A loan available to parents of dependent undergraduate students for which the borrower is fully responsible for paying the interest regardless of the loan status.
Teach Grant Program
Provides grants of up to $4,000 a year to students who are completing or plan to complete course work needed to begin a career in teaching. If you do not meet the requirements of your service obligation, all TEACH Grants you received will be converted to Direct Unsubsidized Loans. You must repay these loans in full, with interest charged from the date of each TEACH Grant disbursement. Service obligation information can be found at https://studentaid.gov/understand-aid/types/grants/teach.
Tuition Payment Plan
An arrangement that divides a student's total education costs (like tuition, fees, housing) into smaller, manageable monthly installments, making it easier to budget and pay over a semester or year, often interest-free, and serving as an alternative to paying the full bill upfront or taking out loans. These plans usually involve an enrollment fee and require automatic payments, with options to pay via bank account or card.
VA Education Benefits
Benefits that help Veterans, service members, and their qualified family members with needs like paying college tuition, finding the right school or training program, and getting career counseling. You can find more information here: https://www.va.gov/education/.

